
Poor water supply impacts health by causing acute infectious diarrhea, repeat or chronic diarrhea episodes, and non-diarrhoeal disease, which can arise from chemical species such as arsenic and fluoride.

Implications of inadequate supply of water
lose electrons) and become iron (III) cations which forms hydrated iron (III) oxide – which is rust. Under normal circumstances, the iron would oxidize (i.e. This is because the more reactive metal zinc (as shown in the reactivity series) will form ions more readily than iron. When the zinc coating of galvanized steel falls apart, the steel will still not rust due to sacrificial protection. Galvanising This is coating with zinc and has the great advantage of sacrificial protection (more info below).Planting – Cans of food are plated with tin.Coating with plastic – Such as freezers, garden furniture etc.Using oil or grease – Effective for moving parts of machinery to be used as a lubricant and a protective coating.Painting – For example, cars, ships, bridges etc.Most methods of rust prevention involve coating the iron or steel in order to prevent contact with water and oxygen: Therefore both oxygen and water must be present for rusting to occur. Rusting is essentially a redox reaction whereby iron reacts with the air and water to form hydrated iron (III) oxide. The term rusting is specific to iron or steel. Rusting is the red/orange coating that forms on the surface of iron when exposed to air and moisture. Nitrogen and carbon dioxide are fairly harmless, and these gases leave the car exhaust. Catalytic converts can reduce pollution by catalyzing the reactions below: Oxides of nitrogen and carbon monoxide are pollutants produced by motor vehicles. Liquid oxygen collects at the bottom of the column.Gaseous nitrogen rises to the top where it is piped off at stored.Liquid nitrogen boils at the bottom of the column.Column warmer at the bottom than the top.Liquid air passed into bottom of fractionating column.Fractional distillation (of liquid air).

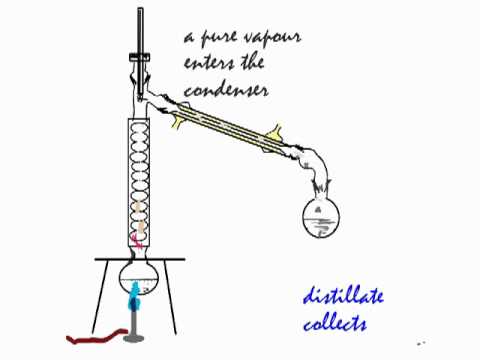
Cooled to -200 degrees to make gas air into liquid.Nitrogen and oxygen can be separated from air by liquefying air first and then separating the two gases via fractional distillation. The composition of clean, dry air is approximately 78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen, and the remaining 1% is a mixture of noble gases and carbon dioxide.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
